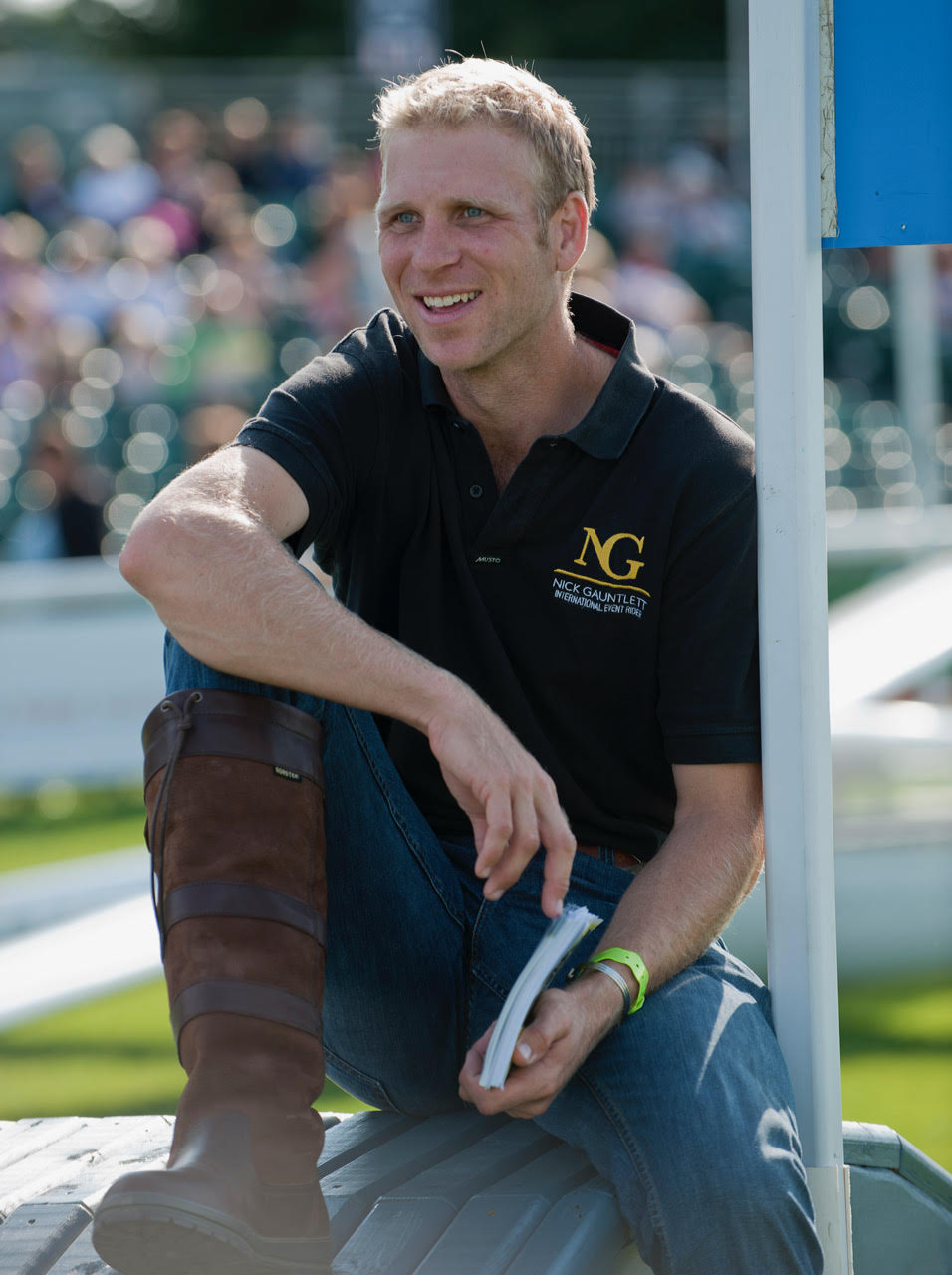
In the first part of our “Trainers in Focus” Series, we catch up with popular trainer Nick Gauntlett. Nick is “a fellow of the British Horse Society” which means he holds the highest level of BHS coaching qualification and is also is one of a small and illustrious group to hold the title of “British Eventing Master Coach”. On top of that, he has competed at the highest level for a number of years and was the rider responsible for producing the great stallion, Chilli Morning to four star level.
What are the key things you focus on when teaching jumping?
Rhythm and energy. The consistency of these two things is far more important than getting to the right spot at the fence. Even over big fences, if you have great rhythm and energy, you can get away with being a bit off the right spot for take-off. Whereas, you can hit the perfect spot but if you don’t have the rest of it, the jump can feel awkward.
How do you teach riders to find a rhythm and see a stride?
I have a few methods, one is to get them to count in a regular rhythm whilst they approach fences. I also get riders to approach a show jump with their eyes closed or looking away. It works unbelievably well in proving to riders that they don’t need to look at a fence to find a stride.”
How do you know if you have enough energy approaching a fence?
“In terms of energy levels, you have to keep checking that the horse is truly in front of the leg. Imagine if you are driving a Ferrari and you hit the accelerator, you would feel a surge of power. Where as if you are driving an old Land Rover in the wrong gear, it is all going to feel a huge effort. Andrew Nicholson once said “if it feels nice, you’re not going fast enough”. I have changed this to “if it feels nice, you’re not good enough”. So you need to feel you are a bit out of your comfort zone and then there will probably be enough power.”
What are common rider faults which you often see?
The position of the leg and upper body position is often at fault and one that is likely to effect the safety and security of the rider. I tell people to imagine their horse has disappeared from underneath them and ask themselves whether their feet would still support them, whether they are jumping a cross-country fence or down a huge drop. When a rider is ahead of the movement, with their full weight resting on the horse on take-off, the horse’s jump will inevitably be compromised and from a safety point of view, this is a big concern.”
How do you develop a more secure seat?
If you are relaxed and soft in the knee and thigh, you will have a more secure lower leg. Whereas if your knee and thigh is tight, it will become a pivot, which will send the lower leg backwards and the body forwards.
Why is a light seat and soft knee so important?
It is amazing how relaxed you can make a sensitive horse feel by being soft through your knee and thigh and having a light seat. I often see riders, see a stride and then start driving with their seat, three strides out. This frequently ends up with them missing the stride and you send the front of the horses forwards and the back end, backwards. I tell riders to imagine having drawing pins in the seat and knee areas of their saddle, to encourage them to be light

What’s your advice for shaving seconds off your cross-country time?
Many people think it’s just about riding faster but actually, you can save more time by just kicking away from each fence. So think of it as saving a second per fence by just landing and kicking as it gets you back into your rhythm as quickly as possible.
What should I think about when planning the perfect cross-country round?
When deciding your approach to a fence, remember that you have walked the course and understand the problem ahead, whilst it is completely new to the horse.
I put fences into three groups:
- Fence with a sloping profile e.g. steeplechase
- Fence with an upright profile e.g. five bar gate
- Combination fence- rail, ditch rail
Jumping a fence with a sloping profile, a rider should feel confident to let the horse jump out of their stride without changing the rhythm.
Jumping an upright fence- we call these “new old fashioned fences” as we see an awful lot more these days. Course Designers at top level talk about designing to encourage “rider responsibility” and this will trickle down to designing at lower levels. As a rider we need to learn from the outset, to get into that defensive position. Keep the energy but allow the horse to see and assess the fence when approaching an upright.
For a combination fence, you should be thinking about which gear to be in and this depends not just on the type of fence but also the experience of the horse. For example, if you are approaching a rail-ditch-rail, all the horse sees as they approach, is the rail. You need to convey to the horse that there is something a bit different about this. It’s like dropping from fifth to third gear- the car slows down but the revs go wild. You mustn’t take the energy away but you have controlled the speed, allowing the horse to understand what is ahead.
The more experienced the horse, the quicker they understand and react to the problem and yours and your horse’s experience should dictate what gear you choose. If you’re just moving up a level, you probably need to give your horse more time so will need a lower gear.
I always tell riders to be careful watching other riders jump through fences and basing their decision on that. It doesn’t necessarily mean that is right for your horse’s level of experience. Intermediate can be the worse for that as you have horses just moving up from Novice level. Then you also come across a four star horse having a spin and they make it look effortless.

Written by Ellie Kelly